Reza Ferdousia, b, Reza Safdaria , Yadollah Omidib
a Department of Health Information Management, School of Allied-Health Sciences, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran; b Research Centre for Pharmaceutical Nanotechnology, Faculty of Pharmacy, Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Tabriz, Iran.
DOI: 10.1016/j.jbi.2017.04.021
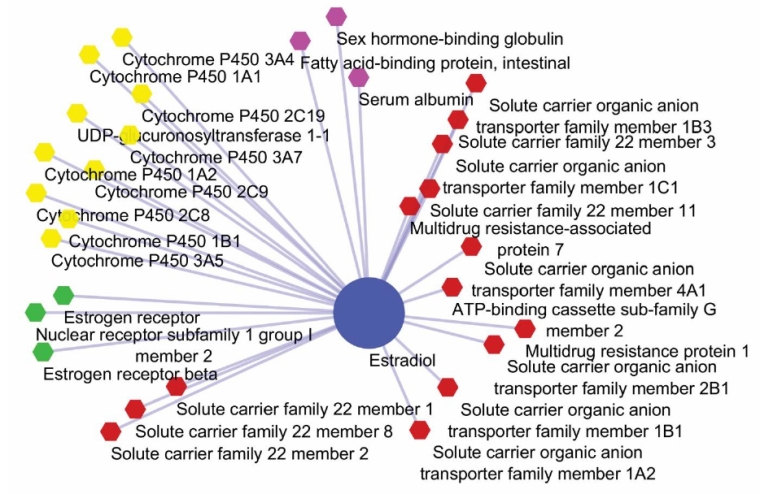
Therapeutic activities of drugs are often influenced by co-administration of drugs that may cause inevitable drug-drug interactions (DDIs) and side effects. Prediction and identification of DDIs are extremely vital for patient safety and success of treatment modalities. A number of computational methods have been employed for the prediction of DDIs based on drugs structures and/or functions. Here, we report on a computational method for DDIs prediction based on functional similarity of drugs. The model was set based on biological elements including carriers, transporters, enzymes and targets (CTET). The model was applied for 2 189 approved drugs. For each drug, all the associated CTETs were collected, and the corresponding binary vectors were constructed to determine the DDIs. Various similarity measures were conducted to detect DDIs. Of the examined similarity methods, the inner product-based similarity measures (IPSMs) were found to provide improved prediction values. Altogether, 2 394 766 potential drug pairs interactions were studied. The model was able to predict over 250 000 unknown potential DDIs. Upon our findings, we propose the current method as a robust, yet simple and fast, universal in silico approach for identification of DDIs. We envision that this proposed method can be used as a practical technique for detection of possible DDIs based on functional similarities of drugs.

